Understanding the Root Cause: The Main Culprits Behind Bone Loss in Teeth
Bone loss in teeth is a common dental problem that occurs due to various reasons. Primarily, it happens when the jawbone surrounding the teeth erodes, causing the teeth to loosen and ultimately fall out. The leading cause of bone loss is periodontal disease, which occurs when bacteria in dental plaque infect the gums and cause inflammation. This inflammation can lead to the destruction of the tooth-supporting tissues, including the bone. Other reasons for bone loss in teeth include trauma, poor dental hygiene, hormonal changes, and genetic factors. If left untreated, bone loss can result in the loss of teeth, difficulty in chewing, and even affect the overall structure of the face. Therefore, it is crucial to take preventative measures, such as regular dental check-ups, proper oral hygiene, and prompt treatment of any dental issues, to maintain healthy bone and teeth.
Understanding the root cause of bone loss in teeth is crucial for effective treatment and prevention. It allows dentists to identify and address the underlying factors that contribute to bone loss, such as gum disease, tooth decay, or injury. By treating the root cause, dentists can not only stop the progression of bone loss but also promote healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Failure to understand the root cause can lead to ineffective treatments that only mask the symptoms without addressing the underlying issue, resulting in further bone loss and potential tooth loss. Therefore, investing time and resources in understanding the root cause of bone loss in teeth can have significant long-term benefits for the patient’s oral health and overall well-being.
Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease is a chronic bacterial infection that affects the tissues and bone that support the teeth. It is caused by the buildup of bacteria and plaque on the teeth and gums, which can lead to inflammation and infection. Over time, if left untreated, periodontal disease can cause bone loss, tooth loss, and other serious health problems. The early stages of periodontal disease are often painless, which is why it is important to have regular dental checkups to catch it early. Symptoms may include swollen or bleeding gums, bad breath, and loose teeth. There are several risk factors for periodontal disease, including smoking, poor oral hygiene, genetics, and certain medical conditions such as diabetes. Treatment for periodontal disease depends on the severity of the condition, but may include deep cleaning, medication, and surgery. It is important to take steps to prevent periodontal disease by brushing and flossing regularly, avoiding tobacco products, and seeing a dentist regularly. By taking care of your oral health, you can prevent periodontal disease and maintain strong, healthy teeth and gums.
Periodontal disease is a common condition affecting the gums and bone supporting teeth, caused by bacterial infection. This infection triggers an immune response that can lead to chronic inflammation, resulting in the destruction of the bone and soft tissue structures that hold teeth in place. As the disease progresses, the bone loss can become significant enough to cause tooth mobility and even tooth loss. The impact of periodontal disease on bone loss is significant because the bone is the foundation for teeth, and without it, teeth cannot be maintained. Therefore, early detection and treatment of periodontal disease is crucial in preventing bone loss and preserving oral health.
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a common condition that results from an inflammation of the tissues surrounding the teeth. There are several risk factors that can contribute to the development of this disease, including poor oral hygiene, smoking, diabetes, genetics, and certain medications. Poor oral hygiene, such as irregular brushing and flossing, can cause the buildup of plaque and tartar, leading to the development of periodontal disease. Smoking is another significant risk factor, as it impairs the body’s ability to fight infections and reduces blood flow to the gums. Diabetes, a chronic condition that affects blood sugar levels, can also increase the risk of periodontal disease, as high blood sugar levels can weaken the immune system and make it more difficult for the body to fight infections. Additionally, genetics can play a role, as some people may be more susceptible to periodontal disease due to their genetic makeup. Finally, certain medications, such as anticonvulsants and blood pressure medications, can also increase the risk of developing periodontal disease.
Prevention and treatment options are crucial in mitigating bone loss in teeth. Preventive measures include adequate oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing and flossing, limiting sugar intake, and avoiding tobacco products. Adequate nutrition, specifically calcium and vitamin D, is also essential in maintaining strong teeth and bones. In cases where bone loss has already occurred, treatment options such as bone grafting, guided tissue regeneration, and dental implant placement can help restore lost bone and improve oral health. Early detection and prompt treatment can prevent further damage and improve long-term outcomes.
Tooth Loss

Tooth loss is a dental problem that affects people of all ages. It can be caused by several factors, including gum diseases, tooth decay, and accidents. Gum diseases are the most common cause of tooth loss, and they occur when bacteria accumulate in the gum tissues, leading to inflammation and eventually tooth loss. Tooth decay is another significant cause of tooth loss, and it occurs when the bacteria in the mouth feed on the food particles left after eating, producing acid that erodes the tooth enamel. Accidents that cause tooth fractures or dislodgment are also a common cause of tooth loss. Tooth loss can have significant impacts on a person’s oral health, including bone loss in the jaw. The jawbone supports the teeth, and when a tooth is lost, the bone surrounding it starts to deteriorate. This deterioration can weaken the jawbone, leading to further tooth loss, and compromising the structural integrity of the entire mouth. Additionally, tooth loss can also affect a person’s self-esteem and confidence, making it difficult for them to interact with others. Therefore, it is essential to take preventive measures to avoid tooth loss, such as maintaining good oral hygiene, visiting the dentist regularly, and wearing protective equipment during high-risk activities.
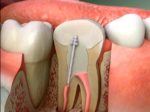
Tooth loss can lead to bone loss due to the lack of stimulation that the tooth root provides to the jawbone. The roots of our teeth help to stimulate the bone and keep it healthy. When a tooth is lost, the underlying bone is no longer stimulated, which causes it to weaken and shrink. This process is called resorption, and it can lead to a decrease in bone density and volume over time. Additionally, the remaining teeth may shift and cause further damage to the jawbone. The longer a missing tooth is left untreated, the more severe the bone loss can become. Therefore, it is essential to address tooth loss promptly to prevent further complications.
Replacing missing teeth is crucial for maintaining proper oral health and overall well-being. When a tooth is missing, the jawbone in that area begins to deteriorate, causing bone loss. This can lead to a range of problems, from difficulty chewing and speaking to a shifting of the remaining teeth. Additionally, missing teeth can have a significant impact on a person’s self-esteem and confidence. Replacing missing teeth with dental implants, bridges or dentures can help prevent bone loss, restore proper function, and enhance a person’s overall quality of life. It is important to seek professional dental advice and treatment to prevent further damage to the jawbone and surrounding teeth.
Missing teeth can be a source of embarrassment, discomfort, and can even lead to bone loss in the jaw. Luckily, there are several treatment options available. Dental implants are a popular option that involves surgically placing a titanium post into the jawbone and attaching a prosthetic tooth. Bridges are another option that involve attaching a prosthetic tooth to adjacent teeth with crowns. Dentures, both partial and complete, are removable prosthetic devices that can replace one or multiple missing teeth. In some cases, bone grafting may be necessary to rebuild the jawbone before implant surgery can be performed. It’s important to consult with a dentist to determine the best treatment option for each individual case.
Osteoporosis

Osteoporosis is a condition that affects the bones, causing them to become weak and brittle. This disease occurs when the body doesn’t produce enough bone tissue or when it loses too much of it. As a result, bones can break easily, leading to fractures, especially in the hip, spine, and wrist. Osteoporosis is a common condition, particularly among older people, and it can cause significant pain, discomfort, and loss of function. The condition is more prevalent in women than men, and it’s estimated that one in three women over the age of 50 will experience osteoporotic fractures. Several factors contribute to the development of osteoporosis, including genetics, hormonal changes, and lifestyle factors. For example, women who experience early menopause or who have had their ovaries removed are at greater risk of developing osteoporosis due to decreased estrogen levels. Other risk factors include excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, and a diet that’s low in calcium and vitamin D. In addition, some medications, such as corticosteroids, can increase the risk of bone loss. To prevent or manage osteoporosis, it’s essential to maintain a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Osteoporosis is a degenerative bone disease that affects the overall bone density and strength, leading to a higher risk of fractures and bone loss. The condition is more common among women, especially those who have gone through menopause, but it can also affect men. Osteoporosis can have a significant impact on the teeth, as the jawbone is one of the most affected areas. The loss of bone density and strength in the jawbone can lead to tooth loss and a higher risk of dental problems. Additionally, osteoporosis can cause a loss of height and a hunched posture, which can further aggravate dental issues by changing the bite alignment and affecting the jaw’s ability to function properly. Therefore, understanding the root cause of bone loss and taking preventive measures is crucial to maintaining good oral health in patients with osteoporosis.
Osteoporosis is a medical condition characterized by low bone mass and bone tissue deterioration, leading to increased bone fragility and susceptibility to fractures. Several risk factors contribute to the development of osteoporosis, including age, gender, genetics, lifestyle, and medical conditions. Aging is one of the primary risk factors for osteoporosis, as bone density tends to decrease with age. Women are at a higher risk of developing osteoporosis than men, especially after menopause, due to the decline in estrogen levels. Genetics also play a crucial role in the development of osteoporosis, as the condition often runs in families. Lifestyle factors such as a sedentary lifestyle, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and poor diet also increase the risk of developing osteoporosis. Medical conditions such as hormonal imbalances, autoimmune disorders, and certain medications can also contribute to the development of osteoporosis.
Prevention and treatment options for bone loss in teeth are essential to maintaining oral health. Regular dental checkups, good oral hygiene practices, and a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D are preventative measures that can help reduce the risk of bone loss. Treatment options include scaling and root planing, bone grafting, and periodontal surgery, depending on the severity of the condition. Medications such as bisphosphonates may also be prescribed to slow down bone loss. However, it is important to identify the root cause of the condition to prevent it from recurring. Proper diagnosis and treatment by a dental professional can help prevent bone loss and promote overall oral health.
Genetics
Genetics plays a significant role in determining the health of an individual’s teeth and bones. The genetic makeup of an individual can influence the development and structure of the jawbones and teeth, making them susceptible to bone loss. Certain genetic conditions, such as osteogenesis imperfecta and amelogenesis imperfecta, can affect the strength and structure of the teeth, leading to tooth loss and bone degradation. Inherited genetic mutations can also affect the production of collagen, a crucial protein that provides strength and support to the bones and teeth. Genetic testing can help identify individuals who are at a higher risk for developing bone loss and other dental issues, allowing for earlier intervention and treatment. The impact of genetics on bone loss in teeth highlights the importance of preventive measures such as maintaining good oral hygiene practices and a healthy diet. While genetics may predispose individuals to certain dental issues, lifestyle factors such as smoking and poor diet can exacerbate these issues and contribute to bone loss. It is essential to work closely with dental professionals to develop an individualized plan that takes into account both genetic and lifestyle factors. Early detection and intervention can help mitigate the impact of genetics on bone loss and improve overall dental health outcomes.
Genetics can significantly contribute to bone loss in teeth. Inherited traits can affect the structure and function of the bone, including the jawbone, which supports the teeth. For example, variations in genes that regulate bone formation and resorption can influence bone density and strength, which can impact the resilience of the jawbone to tooth loss. Additionally, genetic factors can influence the risk of developing conditions that affect bone health, such as osteoporosis. Therefore, understanding the genetic underpinnings of bone loss can provide insights into how to prevent, diagnose, and treat dental conditions related to bone loss.
There are several genetic conditions that can lead to bone loss, including osteogenesis imperfecta, Marfan syndrome, and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Osteogenesis imperfecta is a rare disorder that causes brittle bones and can lead to fractures, while Marfan syndrome affects the body’s connective tissue and can cause bone deformities. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, on the other hand, affects the body’s collagen and can lead to joint pain and bone fragility. These conditions can have a significant impact on an individual’s bone health and may require specialized treatment to prevent further bone loss. It is important for individuals with these genetic conditions to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a comprehensive plan to manage their bone health.
Prevention and treatment options for bone loss in teeth vary depending on the root cause. Good oral hygiene, including regular brushing and flossing, can prevent gum disease and subsequent bone loss. Calcium and vitamin D supplements, as well as a diet rich in these nutrients, can help maintain bone density. For those already experiencing bone loss, treatments such as bone grafts and guided tissue regeneration can help regenerate lost bone. In severe cases, dental implants may be necessary to replace lost teeth and restore proper function to the mouth. It is important to consult with a dental professional to determine the best course of action for addressing bone loss in teeth.
Bone loss in teeth can be caused by a variety of culprits, including periodontal disease, tooth decay, and trauma. Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is one of the most common causes of bone loss. It occurs when harmful bacteria build up in the gum tissue, leading to inflammation and infection. Over time, this can cause the gums to recede and the bone beneath to deteriorate. Tooth decay can also lead to bone loss, particularly if left untreated for an extended period. Trauma, such as a sports injury or accident, can also damage the bone around a tooth, leading to bone loss. Understanding these main culprits behind bone loss in teeth can help individuals take steps to prevent and treat the condition.
Early detection and treatment of bone loss in teeth is crucial to prevent further damage and complications. Identifying the root cause of bone loss, whether it be gum disease, poor oral hygiene, or other underlying health conditions, is key to developing an effective treatment plan. The longer bone loss goes untreated, the greater the risk of tooth loss and other serious health problems, such as infections and heart disease. Early intervention can help to halt or even reverse bone loss, preserving the health and functionality of teeth and supporting structures. Regular dental check-ups, good oral hygiene habits, and a healthy lifestyle all play important roles in preventing and managing bone loss in teeth.
The article \Understanding the Root Cause: The Main Culprits Behind Bone Loss in Teeth\ provides a comprehensive overview of the factors that contribute to bone loss in teeth. The author highlights the importance of maintaining good oral hygiene, consuming a healthy diet, and avoiding harmful habits such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. The article also emphasizes the role of genetics, hormones, and age in bone loss. The overall message of the article is that bone loss in teeth is a complex issue that requires a multifaceted approach to prevention and treatment. By taking proactive steps to prevent bone loss, individuals can maintain good oral health and avoid the negative consequences of tooth loss.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the root cause of bone loss in teeth is crucial for maintaining optimal oral health. The main culprits behind this condition include poor oral hygiene, periodontal disease, smoking, hormonal changes, and certain medical conditions. It is essential to take proactive measures to prevent bone loss, such as practicing good oral hygiene, quitting smoking, and seeking prompt treatment for any underlying medical conditions. By prioritizing oral health and addressing any early signs of bone loss, individuals can preserve their teeth and enjoy a healthy smile for years to come.