When Do Puppies Lose Their Canine Teeth? A Guide to Your Puppy’s Dental Development
Puppies go through various stages of development in their first year of life, and their dental growth is an important part of this process. Like human babies, puppies are born without teeth, but their teeth start to emerge within a few weeks after birth. As they grow older, puppies lose their baby teeth and develop their adult teeth. Understanding the timeline of your puppy’s dental development can help you take better care of their teeth and ensure they have a healthy mouth throughout their life. One of the most significant milestones in a puppy’s dental development is the loss of their canine teeth. Canine teeth, also known as fangs, are the sharp, pointed teeth located next to the incisors in a puppy’s mouth. These teeth are essential for a puppy’s ability to grasp and tear food. However, as the puppy grows and their mouth expands, their baby canine teeth are eventually replaced with adult canine teeth. Knowing when this transition occurs can help you determine if your puppy’s dental development is on track and identify any potential problems that may require a vet’s attention.
Puppy dental development is an essential aspect of their overall health and well-being. During the first few months of a puppy’s life, their teeth go through various stages of development, including the eruption of their baby teeth and the eventual loss of these teeth to make room for their adult teeth. Proper dental care during this time is crucial to prevent dental problems such as tooth decay, gum disease, and bad breath. It is also important to monitor a puppy’s dental development, as any abnormalities or delays could indicate underlying health issues. By ensuring your puppy receives proper dental care and attention, you can help to maintain their oral health and prevent potential health problems in the future.
The process of puppy dental development is a gradual one, beginning at around three weeks of age when the first baby teeth start to emerge. Over the next few months, the puppy’s baby teeth will continue to come in, with the incisors typically appearing first, followed by the canine teeth and then the premolars. As the puppy grows, it will begin to lose its baby teeth, with the adult teeth taking their place. This process usually starts at around four months of age and can continue until the puppy is around six to eight months old. During this time, the puppy may experience some discomfort, and it’s important to provide them with appropriate chew toys and treats to help ease any pain or discomfort. By understanding the process of puppy dental development, you can ensure that your furry friend has a healthy and happy smile for years to come.
Puppy Teeth Timeline
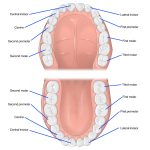
The puppy teeth timeline is an essential part of understanding your furry friend’s dental development. Puppies are born without teeth, but their baby teeth, also known as deciduous teeth, start to emerge between two and four weeks of age. By the time the puppy is eight weeks old, it should have a full set of 28 deciduous teeth. These teeth are relatively small and sharp, designed to help the puppy explore and feed on its mother’s milk. As the puppy grows, it goes through several stages of dental development. At around three to four months old, the puppy’s deciduous teeth start to fall out, making way for the permanent teeth. The first teeth to go are usually the incisors, followed by the canine teeth, and then the premolars. By six to seven months of age, the puppy should have a full set of 42 permanent teeth. It’s essential to keep an eye on your puppy’s teeth during this time to ensure they’re healthy and developing correctly. Regular dental checkups can help identify any issues early, such as retained baby teeth or misaligned permanent teeth that may require intervention from your veterinarian.
The timeline of puppy teeth development is a fascinating process that every dog owner should be aware of. Puppies are born without teeth, but by the time they are two weeks old, their incisors begin to emerge. The canines and premolars follow suit at around four weeks of age, and by eight weeks, they should have a full set of 28 baby teeth. These teeth serve their purpose until the permanent teeth start to emerge at around three to four months of age. The incisors are the first to fall out, followed by the canines and premolars. By the time the puppy is six to eight months old, they should have a full set of 42 adult teeth. It’s essential to monitor your puppy’s dental development as it can affect their overall health and well-being in the long run.
Primary teeth, also known as baby teeth, are the first set of teeth that develop in humans and animals. These teeth usually start to appear around six months of age and continue to erupt until the child is around two or three years old. Primary teeth serve as placeholders for the permanent teeth that will eventually replace them. On the other hand, permanent teeth are the second set of teeth that develop in humans and animals. These teeth start to replace the primary teeth around age six or seven and continue to emerge until the late teens or early twenties. Permanent teeth are larger and stronger than primary teeth and are designed to last a lifetime. They play an essential role in chewing, speaking, and maintaining the structure of the mouth and jaw. Proper dental care and regular check-ups are crucial to maintain healthy primary and permanent teeth.
A chart or diagram of the puppy teeth timeline can be a helpful tool for pet owners to understand their puppy’s dental development. This timeline typically begins with the eruption of the incisors at around 3-4 weeks old, followed by the canines at 4-5 weeks old. At 3-4 months old, the puppy’s premolars will start to come in, and by 6-7 months old, the adult molars should have fully erupted. Throughout this process, it’s important for pet owners to monitor their puppy’s teeth and oral health, as issues like retained baby teeth or improper alignment can cause problems down the line. By understanding the puppy teeth timeline, pet owners can better care for their furry friend’s dental health and set them up for a lifetime of healthy teeth and gums.
Canine Teeth Development

Canine teeth development in puppies is a natural process that occurs as their bodies grow and mature. These teeth are the long, pointed teeth located on either side of the front incisors, and they are used for tearing and gripping food. Puppies are born without canine teeth, and they typically begin to grow around 3-4 weeks of age. These teeth will continue to develop and erupt over the next several months, with the permanent canine teeth typically fully developed by 6-7 months of age. During the canine teeth development process, puppies may experience some discomfort as the teeth erupt through the gums. As a result, they may chew on objects more frequently in an attempt to relieve the pressure. It is important for puppy owners to provide their puppies with appropriate chew toys to help alleviate discomfort and prevent destructive chewing behavior. Additionally, regular dental check-ups with a veterinarian can ensure that the puppy’s teeth are developing properly and that any potential dental issues are addressed early on. Understanding the process of canine teeth development can help puppy owners provide appropriate care for their furry friends during this important stage of growth.
Canine teeth, also known as cuspids, are the pointed teeth located in the front of a dog’s mouth. These teeth are designed for gripping and tearing food, as well as for self-defense in the wild. Canine teeth are longer and sharper than the other teeth, and are present in both the upper and lower jaw. Puppies are born without teeth, but their canine teeth typically begin to emerge around four weeks of age. Over the next few months, puppies will lose their baby teeth and their adult teeth will grow in. Canine teeth are an important part of a dog’s dental development, and should be regularly checked and cleaned to ensure good dental health.
Canine teeth are important for a puppy’s dental development as they are used for biting and tearing food. Puppies typically develop their first set of canine teeth, also known as \milk teeth,\ between the ages of 3-4 weeks old, along with their incisors. As they grow, puppies will develop a total of 28 deciduous teeth, which will eventually fall out to make room for their permanent teeth. Canine teeth are particularly important because they are larger and sharper than other teeth, allowing puppies to break down and consume food more easily. It is important for pet owners to monitor their puppy’s dental development and provide proper care to ensure healthy teeth and gums throughout their dog’s life.
As a puppy ages, there are several signs that indicate the development of their canine teeth. One of the most noticeable indicators is when the puppy begins to chew on everything in sight, including furniture, shoes, and even their owner’s fingers. This behavior is a result of the discomfort and itching caused by the new teeth pushing through the gums. Additionally, puppies may experience a slight loss of appetite, as their gums become sore and tender. They may also exhibit a tendency to drool more than usual, which can further contribute to the discomfort associated with teething. As a responsible pet owner, it’s important to provide your puppy with appropriate chew toys and ensure that they receive regular dental care to support their overall health and well-being.
Losing Canine Teeth
Losing canine teeth is a natural process that occurs in all puppies. Canine teeth are important teeth that are used for biting and tearing food, as well as for self-defense. These teeth are long and pointed and are located at the front of the mouth, next to the incisors. Puppies have a total of four canine teeth, two on the top and two on the bottom. These teeth are typically the last baby teeth to fall out, and they are usually replaced by permanent teeth when the puppy is between four and six months old. During the teething process, puppies may experience discomfort and pain as their baby teeth fall out and their permanent teeth come in. As a result, they may chew on objects to relieve the discomfort. It is important to provide puppies with appropriate chew toys to prevent them from chewing on inappropriate objects, such as furniture or shoes. Additionally, it is important to maintain good dental hygiene during this time to prevent dental problems from developing. Regular brushing and dental check-ups can help keep your puppy’s teeth and gums healthy and prevent future dental issues.
Puppies, like human babies, lose their primary (baby) teeth as they grow and develop into adult dogs. This process is known as teething and it starts when puppies are around three to four months old. As their adult teeth begin to grow and push against their baby teeth, the roots of the baby teeth start to dissolve, causing them to become loose and fall out. This allows room for the adult teeth to come in and take their place. The process can be uncomfortable for puppies and they may experience symptoms such as chewing on objects, drooling, and irritability. It’s important for owners to provide their puppies with appropriate chew toys and to monitor their dental development to ensure that their adult teeth come in properly.
As adorable as puppies are, they go through a lot of changes in their first few months of life, including losing their primary (baby) teeth. This typically happens around three to six months of age, just as their adult teeth are starting to come in. The process of losing their baby teeth can be uncomfortable for puppies, and they may experience some pain or soreness as their teeth loosen and fall out. However, it’s important to let the process happen naturally and not try to pull the teeth out yourself, as this can cause even more discomfort for your furry friend. Keeping an eye on your puppy’s dental development and providing appropriate toys and chews can help ensure they have a healthy mouth as they grow into adulthood.
Puppyhood is an exciting time for pet parents, as they witness their furry friends grow and develop. One of the most significant milestones in a puppy’s life is the loss of its primary teeth. This process starts at around 3-4 months of age and can continue until they are around 7 months old. You may notice signs such as increased chewing, bleeding gums, bad breath, and loose teeth. Your puppy may also become more irritable or avoid certain types of food. It’s important to monitor your puppy’s dental development and provide them with appropriate chew toys and dental treats to help ease any discomfort they may experience during this time.
Caring for Puppy Teeth
Caring for Puppy Teeth is an essential aspect of overall pet health. Puppies, like human babies, go through a teething process that can be uncomfortable and painful. During this time, it is crucial to keep a close eye on your puppy’s oral hygiene to ensure that their teeth stay healthy and strong. One way to care for your puppy’s teeth is to brush them regularly with a toothbrush and toothpaste designed for dogs. This should be done at least once a day, and preferably after every meal. You can also give your puppy dental chews or toys that help remove plaque and tartar buildup. These chews and toys are specifically designed to be gentle on puppy teeth and gums. Another way to care for your puppy’s teeth is to provide them with a healthy diet that promotes dental health. A diet rich in calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin D is essential for healthy teeth and bones. You can also give your puppy raw bones or dental treats that help clean their teeth while they chew. When caring for your puppy’s teeth, it is important to avoid giving them human food or treats that are high in sugar, as this can lead to tooth decay and other oral health problems. By taking a proactive approach to dental care, you can help ensure that your puppy grows up with healthy teeth and gums.
Caring for your puppy’s teeth is an essential part of their overall health and well-being. To ensure healthy dental development, it is recommended to start brushing your puppy’s teeth as early as possible. Using a soft-bristled toothbrush and dog-specific toothpaste, gently brush your puppy’s teeth in a circular motion. Additionally, providing your puppy with appropriate chew toys can help clean their teeth and relieve teething discomfort. Avoid giving your puppy hard or excessively sticky treats, as these can damage their teeth. Regular veterinary check-ups can also help detect any dental issues early on and prevent more serious problems down the line. By taking care of your puppy’s teeth, you can help ensure a lifetime of healthy smiles.
Dental hygiene is just as important for puppies as it is for adult dogs. Regular brushing and dental care can prevent a host of dental issues, including periodontal disease, tooth decay, and bad breath. Puppies, in particular, are susceptible to dental problems because they are still developing their teeth and jaws. By establishing good dental hygiene habits early on, you can help your puppy maintain healthy teeth and gums throughout their life. This includes regular brushing, dental check-ups, and providing appropriate chew toys to help keep their teeth clean and strong. By taking care of your puppy’s teeth, you can help ensure that they grow up with a healthy, happy smile.
Brushing your puppy’s teeth is an important part of their dental hygiene and should be started early to get them used to the process. First, choose a toothbrush and toothpaste specifically designed for dogs. Gently lift your puppy’s lip and brush their teeth using a circular motion, focusing on the gum line where plaque and tartar can build up. Start with just a few teeth at a time and gradually work up to the entire mouth. Be sure to reward your puppy with praise and treats to make the experience positive. It’s recommended to brush your puppy’s teeth at least twice a week to maintain good oral health. Remember, a healthy mouth leads to a healthy pup!
Puppy dental development is a complex process that occurs in stages. At around three weeks old, a puppy’s baby teeth start to appear, and by eight weeks, they should have a full set. As they grow, their baby teeth fall out and are replaced by adult teeth, starting with the incisors at around 12 weeks and finishing with the molars at around six months. During this time, it’s essential to monitor your puppy’s dental health and provide them with appropriate chew toys and dental care to ensure their teeth and gums are healthy, as dental problems can lead to pain, discomfort, and even systemic infections. By understanding the process of puppy dental development, you can help your furry friend maintain healthy teeth and gums throughout their life.
Monitoring a puppy’s dental health is essential to ensure their overall well-being. As puppies grow, their teeth develop, and it is crucial to keep an eye on their dental health throughout this period. Regular checks will help identify any dental issues, such as tooth decay, gum disease or misaligned teeth, which can cause discomfort and pain for the puppy. Additionally, poor dental health can lead to other health problems, such as infections, heart disease, and kidney disease. Therefore, maintaining good dental hygiene, such as brushing teeth regularly, giving them dental chews and toys, and visiting a veterinarian for check-ups, is essential to ensure the puppy’s healthy development and prevent any potential health problems in the future.
Final thoughts and recommendations for puppy dental care are crucial for pet owners to ensure their puppies’ optimal oral health. Regular brushing with puppy-specific toothpaste and a soft-bristled brush can help remove plaque and prevent tartar buildup. Additionally, providing appropriate chew toys and treats can help promote healthy chewing habits and reduce the risk of dental problems. It’s also essential to schedule regular veterinary check-ups to monitor your puppy’s dental development and address any issues early on. By prioritizing your puppy’s dental care, you can help ensure they have a healthy and happy smile for years to come.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the dental development of your puppy is crucial for their overall health and well-being. While puppies will inevitably lose their baby teeth, it is important to monitor their oral health and provide appropriate care to ensure a smooth transition into adulthood. By maintaining good dental hygiene practices and seeking professional veterinary care when necessary, you can help your furry friend grow into a healthy and happy adult dog with a bright and healthy smile. Remember, a little attention to your puppy’s dental development now can go a long way in preventing potential dental issues in the future.