Why Do Teeth Fall Out as We Age? Understanding the Causes of Tooth Loss in the Elderly

As we age, our bodies undergo various changes that affect our health and wellbeing. One of the most common issues that affect the elderly is tooth loss. Losing teeth can have a significant impact on our quality of life, affecting our ability to eat, speak, and smile with confidence. Understanding the causes of tooth loss in the elderly is crucial to prevent this issue and maintain good oral health. Tooth loss can be caused by various factors, including poor oral hygiene, gum disease, and tooth decay. These factors are often interlinked, with poor oral hygiene leading to gum disease, which can cause tooth decay and eventually tooth loss. Other factors that can contribute to tooth loss in the elderly include smoking, certain medications, and chronic illnesses such as diabetes. By understanding the underlying causes of tooth loss, we can take steps to prevent it and maintain good oral health as we age.
As we age, our bodies undergo numerous changes that can affect our oral health. Tooth loss in the elderly is a common phenomenon that can have a significant impact on their quality of life. There are several reasons why teeth fall out as we age, including periodontal disease, poor oral hygiene, gum recession, and physical wear and tear. Additionally, certain medical conditions and medications can also contribute to tooth loss. Understanding the causes of tooth loss in the elderly is crucial for preventing and treating this problem, as well as promoting overall health and wellbeing.
Understanding tooth loss in the elderly is crucial for maintaining their overall health and quality of life. As we age, our teeth become more vulnerable to decay, gum disease, and other dental problems, which can eventually lead to tooth loss. Missing teeth can cause difficulties with eating, speaking, and can even impact self-esteem. Furthermore, tooth loss has been linked to a variety of health problems, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and even dementia. Therefore, it is essential that the elderly receive proper dental care and education on how to maintain good oral hygiene to prevent tooth loss and maintain their overall health and wellbeing.
Natural Aging Process
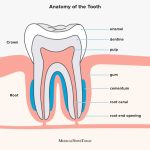
The natural aging process is a gradual and inevitable occurrence that affects all parts of the body, including the teeth. As we age, our teeth undergo various changes that can ultimately lead to tooth loss. One of the most common changes is the wear and tear of the enamel, which is the hard outer layer of the tooth. Over time, the enamel can become thinner, making it more susceptible to decay and damage. Additionally, the gums may recede, exposing the root of the tooth, which can also lead to decay and infection. Another factor that contributes to tooth loss in the elderly is bone loss. As we age, the bones in our body become less dense, including the jawbone that supports our teeth. When the jawbone loses density, it can no longer hold the teeth in place, causing them to loosen and fall out. Furthermore, other health conditions that are more prevalent in older adults, such as diabetes and heart disease, can also affect the health of the teeth and gums. Therefore, it is important for seniors to maintain good oral hygiene and visit the dentist regularly to prevent tooth loss and other dental problems.
As we age, our teeth undergo various changes that can lead to tooth loss. One of the main factors that affect teeth is the natural aging process. As we get older, our teeth become more susceptible to wear and tear, and the enamel that covers the teeth may become thinner, making them more vulnerable to decay. Additionally, the gums may recede, exposing the roots of the teeth to bacteria and infection. The bones that support the teeth may also weaken, making it more difficult for them to stay in place. All of these factors can contribute to tooth loss in the elderly. However, with proper dental care and regular check-ups, many of these issues can be prevented or treated before they become more serious.
As we age, changes in gum tissue and bone structure can lead to tooth loss. Gum tissue may recede and become more fragile, which can expose the roots of teeth and increase the risk of decay and infection. Additionally, bone loss in the jaw can weaken the foundation of teeth, causing them to become loose and eventually fall out. This bone loss can be caused by a variety of factors, including periodontal disease, osteoporosis, and a lack of proper nutrition. Regular dental check-ups and proper oral hygiene can help prevent and address these issues, but it is important to understand that tooth loss is a natural part of aging and can be a sign of larger health concerns.
Saliva plays a crucial role in maintaining oral health, and a decrease in its production can lead to several oral problems. As we age, the saliva-producing glands may not function as efficiently as they used to, leading to dry mouth or xerostomia. This condition can increase the risk of tooth decay, gum disease, and other oral infections, ultimately leading to tooth loss. In addition to age, certain medications, radiation therapy, and autoimmune diseases can also cause a decrease in saliva production. To combat this issue, individuals can try stimulating saliva production through chewing sugar-free gum, sipping water frequently, and avoiding tobacco and alcohol.
Poor Oral Hygiene
Poor oral hygiene is one of the major reasons why teeth fall out as we age. Neglecting the health of your teeth and gums can lead to a host of oral health problems such as cavities, gum disease, and tooth loss. When plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, builds up on your teeth, it can harden into tartar, which can only be removed by a dental professional. If left untreated, tartar can cause gum disease, which can lead to tooth loss. Furthermore, poor oral hygiene habits such as not brushing or flossing regularly, not using mouthwash, or not visiting the dentist for regular cleanings and checkups can exacerbate these problems and lead to irreversible damage to your teeth and gums. Maintaining good oral hygiene is essential for preventing tooth loss as we age. Brushing your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, using mouthwash, and visiting the dentist regularly for cleanings and checkups can help prevent plaque buildup, cavities, and gum disease. Additionally, a healthy diet and lifestyle, including limiting sugary and acidic foods and drinks, can help protect your teeth and gums. By taking these simple steps, you can ensure the health and longevity of your teeth as you age.
Maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial in preventing tooth loss, especially as we age. Poor oral hygiene can lead to the buildup of plaque and bacteria, which can cause gum disease and tooth decay. Gum disease, in particular, is a common cause of tooth loss in older adults as it can cause the gums to recede, exposing the roots of teeth and making them more susceptible to decay. Additionally, neglecting to regularly brush and floss can lead to the development of cavities, which can weaken teeth and ultimately lead to tooth loss. Therefore, it is essential to maintain good oral hygiene habits, such as brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and visiting the dentist regularly, to prevent tooth loss and maintain optimal oral health.
Poor oral hygiene can lead to tooth loss in several ways. When we neglect to brush and floss regularly, plaque and tartar can build up on and between our teeth, leading to tooth decay and gum disease. Over time, this decay can spread to the tooth’s root, causing pain, infection, and ultimately, tooth loss. In addition, gum disease can cause the gums to recede, exposing the tooth’s roots and making them more vulnerable to decay and infection. Finally, poor oral hygiene can also contribute to the development of periodontitis, a serious and chronic form of gum disease that can cause the bone and tissue supporting the teeth to break down, leading to tooth loss. Therefore, it is essential to maintain proper oral hygiene habits to prevent tooth loss and keep our teeth healthy and strong as we age.
Oral hygiene is crucial to maintaining healthy teeth and gums, regardless of age. However, the elderly may struggle with proper dental care due to physical limitations or cognitive impairment. Common mistakes include inadequate brushing or flossing, neglecting to clean dentures, using improper cleaning tools, and consuming sugary or acidic foods and beverages. These habits can lead to gum disease and tooth decay, which can ultimately result in tooth loss. It’s important for the elderly to prioritize their oral health and seek assistance from caregivers or dental professionals if needed to prevent tooth loss and maintain overall well-being.
Gum Disease
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common cause of tooth loss in older adults. It is a bacterial infection that affects the gums and the bone that supports the teeth. Gum disease is caused by a buildup of plaque, which is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. If plaque is not removed by brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar, which can only be removed by a dentist or dental hygienist. Over time, the buildup of plaque and tartar can cause the gums to become inflamed and infected, leading to gum disease. Symptoms of gum disease include red, swollen, and bleeding gums, bad breath, and loose teeth. Untreated gum disease can lead to tooth loss, as the infection can destroy the bone that supports the teeth. In fact, gum disease is the most common cause of tooth loss in adults over the age of 65. However, gum disease is preventable and treatable with good oral hygiene habits and regular dental checkups. Brushing and flossing regularly can remove plaque and prevent tartar buildup. In addition, quitting smoking, eating a healthy diet, and managing conditions such as diabetes can also help prevent gum disease. If gum disease is detected early, it can be treated with a deep cleaning called scaling and root planing, which removes plaque and tartar from below the gumline. In more advanced cases, gum surgery may be necessary to remove infected tissue and prevent further damage to the teeth and gums.
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common dental problem that affects the gums, bones, and tissues surrounding the teeth. It is caused by bacteria found in plaque, which is a sticky film that forms on the teeth and gums. When plaque is not removed through regular brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar, which can only be removed through professional dental cleanings. The bacteria in plaque and tartar can cause inflammation and infection in the gums, leading to gum disease. Other risk factors for gum disease include smoking, hormonal changes, and certain medications. If left untreated, gum disease can progress and lead to tooth loss and other serious health problems.
Gum disease or periodontitis is a serious condition that affects the soft tissues and bones that support the teeth. It starts with the accumulation of plaque on the teeth and gums, which causes inflammation and infection. Over time, the inflammation and infection can spread to the surrounding tissues, causing the gums to recede and the bone to break down. This process weakens the teeth and can eventually lead to tooth loss. In addition, gum disease can cause pockets to form between the teeth and gums, which can harbor bacteria and further exacerbate the condition. If left untreated, gum disease can ultimately result in the loss of one or more teeth, making it important to practice good oral hygiene and seek treatment at the first signs of trouble.
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common cause of tooth loss in the elderly. The early signs of gum disease include red and swollen gums, bad breath, and bleeding gums while brushing or flossing. As the disease progresses, the gums may recede, exposing the tooth roots and leading to sensitivity and pain. Pockets may form between the teeth and gums, allowing bacteria to accumulate and cause further damage. If left untreated, gum disease can cause the teeth to become loose and eventually fall out. Regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene habits are essential for preventing and treating gum disease.
Other Causes of Tooth Loss in the Elderly
Tooth loss in the elderly can occur due to various reasons other than decay and gum disease. One of the most common reasons is a lack of proper nutrition. A diet that is deficient in essential vitamins and minerals can lead to weaker teeth and gums, making them more susceptible to damage and decay. Additionally, certain medications can also have an adverse effect on dental health, leading to tooth loss. Medications such as blood thinners, antihistamines, and antidepressants can cause dry mouth, making it difficult for saliva to neutralize harmful bacteria and acids in the mouth. This, in turn, can lead to tooth decay and gum disease, eventually resulting in tooth loss. Another cause of tooth loss in the elderly is trauma or injury. As we age, our bones become more brittle, and the teeth and gums become weaker. This can make them more susceptible to damage and injury from falls, accidents, or even simple activities like chewing hard foods. Additionally, dental injuries sustained in earlier years can also lead to tooth loss in later life. For example, a person who has had a tooth knocked out or fractured in their youth may develop complications later on in life that result in the loss of that tooth. Overall, it is essential to maintain good dental hygiene and nutrition, avoid harmful medications, and take precautions to prevent dental injuries to reduce the risk of tooth loss in the elderly.
Medications can have a significant impact on dental health, especially in older adults. Certain medications, such as antihistamines, antidepressants, and blood pressure medications, can cause dry mouth, which can lead to tooth decay and gum disease. Additionally, some medications, such as bisphosphonates, which are used to treat osteoporosis, can cause a rare but severe side effect called osteonecrosis of the jaw, which can lead to tooth loss. It is important for individuals taking medications to inform their dentist, who can provide recommendations for maintaining proper dental health.
Medical conditions can significantly increase the risk of tooth loss in older adults. Diabetes, for example, can cause gum disease due to high blood sugar levels, which can lead to inflammation, infection, and bone loss in the jaw. Osteoporosis can also weaken the bones in the jaw, making tooth loss more likely. Additionally, autoimmune diseases such as Sjogren’s syndrome can cause dry mouth, which can lead to tooth decay and gum disease. Cancer treatments such as chemotherapy and radiation can damage the teeth and gums, increasing the risk of tooth loss. Proper management of these medical conditions and regular dental check-ups can help prevent or mitigate tooth loss in older adults.
Tooth loss in the elderly is a common problem that can be attributed to various lifestyle factors. Poor oral hygiene practices such as irregular brushing and flossing can lead to the accumulation of plaque and bacteria, which can cause gum disease and ultimately tooth loss. Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption have also been linked to an increased risk of gum disease and tooth loss. Additionally, a diet high in sugar and processed foods can contribute to tooth decay, which can eventually lead to tooth loss. Finally, certain medical conditions such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease can also increase the risk of tooth loss in older adults. It is important to maintain good oral hygiene habits and a healthy lifestyle to prevent tooth loss as we age.
Tooth loss is a common problem among the elderly, and it can significantly affect their overall health and quality of life. There are several main causes of tooth loss in the elderly, including periodontal disease, decay, and lack of dental care. Periodontal disease, which is a bacterial infection that affects the gums and bone around the teeth, is the leading cause of tooth loss in the elderly. Decay, which is caused by poor oral hygiene and a diet high in sugar, can also lead to tooth loss. Additionally, many elderly individuals do not receive regular dental care, which can result in untreated dental problems that eventually lead to tooth loss. Understanding these causes can help individuals take steps to prevent tooth loss and maintain good oral health as they age.
Maintaining good oral health is crucial throughout life, especially as we age. As we grow older, our teeth and gums become more vulnerable to various oral health problems, such as gum disease, tooth decay, and tooth loss. Poor oral hygiene habits, such as neglecting to brush and floss regularly, can increase the risk of developing these issues. Moreover, certain medical conditions, such as diabetes and osteoporosis, can also affect oral health and contribute to tooth loss. Therefore, it is essential to practice good oral hygiene habits, such as brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and visiting the dentist regularly, to keep our teeth and gums healthy and prevent tooth loss as we age.
To prevent tooth loss in the elderly, it is essential to maintain good oral hygiene through regular brushing and flossing. A healthy diet with a balanced intake of vitamins and minerals is also crucial. Regular dental check-ups can detect dental problems at an early stage, preventing further damage to the teeth and gums. Avoiding tobacco use and limiting alcohol consumption can also help prevent tooth loss. In cases of gum disease, prompt treatment is necessary to prevent tooth loss. Maintaining good overall health and managing chronic health conditions can also contribute to healthy teeth and gums in the elderly. By following these recommendations, the elderly can maintain their oral health and prevent tooth loss, ensuring a better quality of life.
Conclusion

In conclusion, tooth loss is a common occurrence as we age, but it is not an inevitable part of the aging process. Understanding the causes of tooth loss in the elderly can help us take preventative measures to maintain good oral hygiene and preserve our teeth as we age. Factors such as poor dental hygiene, gum disease, and certain medical conditions can contribute to tooth loss, but it is also important to consider lifestyle factors such as diet and smoking. Regular dental check-ups and a healthy lifestyle can go a long way in preventing tooth loss and promoting good oral health throughout our lives. Taking care of our teeth is not just important for our physical health, but it can also boost our confidence and overall well-being.