Doggie Dental: Understanding Which Teeth Your Canine Companion Will Shed
A dog’s dental health is as important as their overall well-being. It is crucial to understand the dental anatomy of dogs and how it evolves as they age. Knowing which teeth your dog will shed and when is essential to ensure their dental hygiene and prevent any potential oral health issues. As a responsible pet owner, it is your duty to familiarize yourself with the teeth shedding process and take the necessary steps to maintain your furry friend’s dental health. In this article, we will delve into the topic of \Doggie Dental: Understanding Which Teeth Your Canine Companion Will Shed.\ We will discuss the different types of teeth in dogs, their functions, and the shedding process. Whether you are a new pet owner or an experienced one, this article will provide valuable insights into your dog’s dental health and equip you with the knowledge to take better care of your furry friend’s teeth. Read on to learn more about doggie dental hygiene and the teeth shedding process.
Understanding canine dental health is crucial for dog owners because it directly affects their pet’s overall well-being. Canine dental issues like gum disease, tooth decay, and bad breath can lead to severe health problems, including heart, kidney, and liver diseases. Regular dental checkups, teeth cleaning, and proper oral hygiene can help prevent such issues and keep dogs healthy. Additionally, dental pain can cause behavioral changes in dogs, such as aggression and depression, which can affect their quality of life and their relationship with their owners. Therefore, by understanding canine dental health, dog owners can ensure their pets’ comfort, happiness, and longevity.
\Doggie Dental: Understanding Which Teeth Your Canine Companion Will Shed\ is an informative article about the dental growth and development of dogs. The article provides a detailed overview of the different types of teeth in dogs, including incisors, canines, premolars, and molars, and explains the typical timeline for when each set of teeth erupts and falls out. It also highlights the importance of maintaining good dental hygiene in dogs to ensure healthy teeth and gums, and provides helpful tips on how to care for your dog’s teeth at home. Overall, this article is an excellent resource for dog owners seeking to better understand their pet’s dental health.
Types of Teeth

Understanding the types of teeth that dogs have can help owners identify potential dental problems and make informed decisions about their pet’s oral health. Dogs have four categories of teeth: incisors, canines, premolars, and molars. Each category has a specific function and shape that enables dogs to chew, grip, and tear their food. The incisors are the small teeth located at the front of the mouth and are used for picking up and holding food. The canines are the long and pointed teeth that are used for gripping and tearing food. The premolars are located behind the canines and are used for crushing and grinding food. Finally, the molars are the large teeth located at the back of the mouth and are used for grinding and chewing food. It is important for dog owners to check their pet’s teeth regularly, as dental problems can lead to pain, infection, and even tooth loss.
Understanding the different types of teeth found in dogs can help pet owners maintain their furry friends’ dental hygiene. Dogs have four different types of teeth, each serving a unique purpose. Incisors are the small front teeth used for grasping and tearing food. Canines, located next to the incisors, are sharp and pointed, used for puncturing and holding onto prey. Premolars, behind the canines, have flat surfaces and are used for chewing and grinding food. Finally, the molars are the largest teeth located at the back of the mouth used to crush and grind food. Knowing the function of each tooth type can help pet owners identify dental problems and take the necessary steps to prevent them.
Just like humans, dogs have different types of teeth that serve different functions when it comes to biting, chewing, and tearing their food. The four different types of teeth that can be found in a dog’s mouth are incisors, canines, premolars, and molars. The incisors, located at the front of the mouth, are used for biting and nibbling. The canines, also known as fangs, are used for tearing and shredding tough meat and bones. The premolars are located behind the canines and are used for grinding and crushing food. Lastly, the molars are located at the back of the mouth and are used for grinding and crushing larger pieces of food. Understanding the different functions of each type of tooth is essential in maintaining your canine companion’s dental health and preventing dental problems such as tooth decay and gum disease.
The Process of Shedding Teeth

Dogs, like humans, go through the process of shedding their baby teeth, which are replaced by their permanent teeth. This process, also known as teething, is a natural and necessary part of a dog’s development. Puppies usually start teething at around 3-4 weeks of age, and by the time they are 6-8 months old, all of their baby teeth will have fallen out and been replaced by permanent teeth. The process of shedding teeth can be uncomfortable for dogs, as the roots of the baby teeth start to dissolve and the teeth become loose. This can cause them to experience pain and discomfort, which may lead to them chewing on things to relieve the discomfort. As a pet owner, it is important to provide your furry friend with safe and appropriate chew toys to help them through this process and prevent them from damaging furniture or other items in your home. Additionally, it is important to maintain good dental hygiene during this time to prevent any infections or other dental issues.
The timeline of canine tooth development in dogs is a gradual and intricate process that begins at birth and continues through their first year of life. Puppies are born toothless, but by two to four weeks, their deciduous teeth begin to emerge. These baby teeth, also known as milk teeth, are 28 in number and include four canines, which are crucial for grasping and tearing food. Between four to six months, the puppy’s adult teeth start to grow, gradually replacing the baby teeth. The canine teeth, also known as fangs, are the last to emerge, usually between five to eight months. Adult dogs have 42 teeth, including four canines that are strong and pointed, designed to help them rip and tear food. Understanding the timeline of canine tooth development is essential for pet owners to ensure their furry friends are healthy and happy.
The process of shedding teeth in dogs, also known as deciduous teeth, is a natural occurrence that happens during a puppy’s growth and development. Typically, puppies start shedding their baby teeth at around three to four months old, and the process continues until they reach six to eight months old. During this period, the roots of the puppy’s baby teeth start to dissolve, eventually causing the teeth to become loose and fall out. In their place, adult teeth will grow to replace them. Dog owners should pay attention to their puppy’s teeth during this time, as retained baby teeth can cause problems such as overcrowding and misalignment of the adult teeth. Regular dental check-ups with a veterinarian can ensure that the process of shedding teeth in dogs is progressing normally.
As puppies grow into adulthood, their teeth go through a significant transformation. The primary teeth, also known as puppy teeth, are temporary and will eventually be replaced by permanent adult teeth. Puppy teeth are smaller, whiter, and have a sharp edge that allows them to chew on soft food. Conversely, adult teeth are larger, stronger, and have a flatter surface that is designed to break down tougher foods. The transition from puppy teeth to adult teeth is a gradual process that occurs between 3-7 months of age, depending on the breed. During this time, puppies may experience discomfort and chew on objects excessively to relieve the pressure. It is essential to monitor your dog’s dental health during this transition period to ensure they develop healthy adult teeth.
Signs of Trouble

As a responsible pet owner, it is important to be aware of the signs of trouble when it comes to your dog’s dental health. Bad breath, swollen or bleeding gums, loose teeth, and difficulty eating are all indications that your furry friend may be suffering from dental problems. It is important to address these issues as soon as possible to prevent further damage and discomfort. Neglecting your dog’s dental health can lead to serious health problems, such as infection, gum disease, and even organ damage. Regular dental check-ups and proper dental care can go a long way in preventing and treating dental problems in dogs. This includes brushing your dog’s teeth regularly, providing dental chews and toys, and scheduling routine dental cleanings with your veterinarian. By monitoring your dog’s dental health and addressing any issues promptly, you can help ensure that your furry friend stays happy and healthy for years to come.
Dental problems in dogs can manifest themselves in a variety of ways. One of the most common symptoms is bad breath, which can be caused by the buildup of plaque and tartar on the teeth. Other signs of dental issues may include swollen or bleeding gums, loose teeth, difficulty eating, or a reluctance to chew on toys or bones. Dogs may also exhibit behavioral changes, such as increased aggression or irritability, due to the discomfort caused by dental problems. It’s important for pet owners to regularly check their dog’s teeth and gums for any signs of trouble and to schedule regular dental check-ups with their veterinarian to ensure their furry friend’s oral health is in tip-top shape.
Regular dental checkups are crucial for maintaining the overall health and well-being of dogs. These checkups can help detect and prevent dental issues before they become severe and expensive to treat. During these checkups, a veterinarian can examine the dog’s teeth and gums for signs of plaque buildup, gum disease, or tooth decay. They can also provide advice on how to properly care for your dog’s teeth at home, including brushing and proper nutrition. Neglecting a dog’s dental health can lead to bad breath, tooth loss, and even serious health problems such as heart disease. Therefore, it is vital to prioritize regular dental checkups for your furry friend to ensure their longevity and comfort.
Maintaining your dog’s dental hygiene is crucial for its overall health. There are several tips that you can follow to keep your furry friend’s teeth healthy. Firstly, provide them with a balanced and nutritious diet that includes dental chews and treats meant for dogs. Secondly, brush their teeth regularly with a dog-specific toothpaste and toothbrush. Thirdly, schedule regular dental checkups with your veterinarian to catch any potential dental issues before they become severe. Lastly, avoid giving your dog hard and chewy toys that can damage their teeth. By following these tips, you can ensure that your canine companion maintains healthy teeth and gums for a long time.
\Doggie Dental: Understanding Which Teeth Your Canine Companion Will Shed\ is an informative article that highlights the importance of dental care for dogs and sheds light on the process of shedding teeth in canines. The article emphasizes the significance of regular dental check-ups and cleaning to prevent dental diseases and tooth loss in dogs. The author explains the different types of teeth in dogs and how they serve various functions. Furthermore, the article focuses on the shedding process of deciduous teeth in puppies and how to recognize the signs of shedding. The writer also discusses the importance of monitoring the growth of permanent teeth and the potential dental problems that can arise if not addressed in time. Overall, the article provides valuable information and insights for dog owners to ensure optimal dental health for their furry companions.
Maintaining good dental health in dogs is crucial for their overall well-being. Dental diseases not only cause pain and discomfort for our furry friends but can also lead to more serious health issues, such as heart disease and kidney damage. Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings, along with a proper dental hygiene routine at home can help prevent these issues. It’s also important to pay attention to the signs of dental problems in dogs, such as bad breath, swollen gums, and difficulty eating, and to seek veterinary care promptly if any issues arise. By taking care of our dog’s dental health, we can ensure they live happy and healthy lives.
Conclusion
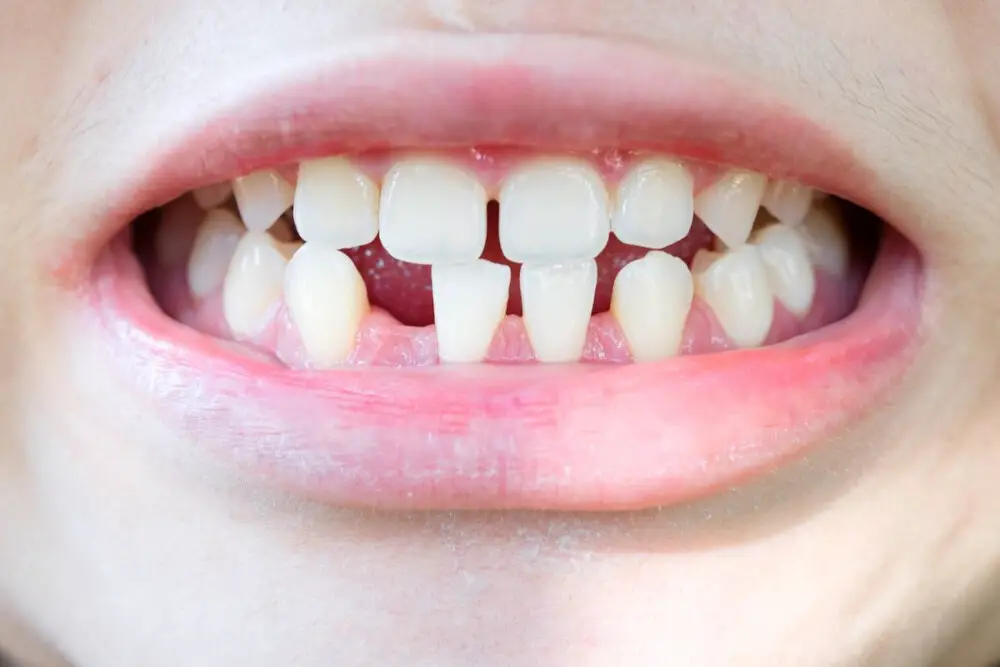
In conclusion, it is essential to understand the process of shedding teeth in dogs to ensure their dental health. Knowing which teeth will fall out and when can help pet owners identify potential dental problems and take the necessary measures to prevent them. Regular dental check-ups and proper dental hygiene practices, including brushing and cleaning, can go a long way in maintaining your furry friend’s oral health. Remember, a healthy mouth leads to a healthy dog, and a healthy dog leads to a happy pet owner. So take care of your dog’s dental health, and their wagging tail will thank you!