Table of Contents
An abscessed tooth is a painful and potentially dangerous dental condition that occurs when bacteria infect the root of a tooth. If left untreated, an abscess can cause severe pain, swelling, and even spread to other parts of the body. In some cases, an abscess can even rupture or “pop,” which can be both painful and alarming. In this article, we’ll discuss what to do if your abscessed tooth pops, including steps you can take to treat the condition and prevent it from recurring.

Section 1: Understanding Abscessed Teeth
- Definition of an abscessed tooth and its causes
An abscessed tooth is a dental condition that occurs when bacteria infect the root of a tooth, leading to the formation of a pocket of pus in the surrounding tissues. The condition can be caused by a variety of factors, including tooth decay, gum disease, trauma to the tooth, and a weakened immune system. When the bacteria multiply, they can create an abscess that can cause severe pain and swelling, and if left untreated, can lead to serious complications. It is essential to seek prompt treatment if you suspect you have an abscessed tooth to prevent the spread of infection and preserve your dental health.
- Signs and symptoms of an abscessed tooth
The signs and symptoms of an abscessed tooth can vary depending on the severity of the infection. Some common signs and symptoms of an abscessed tooth include:
- Tooth pain that is severe, constant, and throbbing in nature.
- Swelling and tenderness in the gums near the affected tooth.
- Sensitivity to hot or cold foods and drinks.
- Difficulty chewing or biting due to pain and discomfort.
- Foul taste or odor in the mouth.
- Fever and general feeling of being unwell.
- Redness or swelling in the face or neck.
- Swollen lymph nodes.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to seek prompt dental treatment to prevent the abscess from worsening and potentially leading to serious complications.
- The dangers of leaving an abscess untreated
Leaving an abscessed tooth untreated can lead to several serious dental and overall health problems. Some of the potential dangers of leaving an abscess untreated include:
- Spread of infection: An abscess is a pocket of pus that can continue to grow and spread if left untreated. The infection can spread to nearby teeth, gums, or even to the jawbone, causing significant damage.
- Tooth loss: An abscessed tooth that is left untreated can cause significant damage to the tooth and surrounding tissues. In some cases, the tooth may become so damaged that it cannot be saved and must be extracted.
- Sinus infection: In some cases, an abscessed tooth can cause a sinus infection if the infection spreads to the sinuses located above the affected tooth.
- Systemic infection: If the infection from an abscessed tooth spreads beyond the oral cavity, it can cause a serious systemic infection, which can lead to hospitalization or even be life-threatening.
- Increased risk of heart disease: Recent studies have suggested a link between untreated dental infections and an increased risk of heart disease.
In short, leaving an abscess untreated can have serious and potentially life-threatening consequences. If you suspect you have an abscessed tooth, it is essential to seek prompt dental treatment to prevent complications and preserve your overall health.
Section 2: What to Do When Your Abscessed Tooth Pops
- Why an abscessed tooth might pop
An abscessed tooth can sometimes rupture or “pop” due to the pressure that builds up inside the pocket of pus. The pressure can be caused by the accumulation of bacteria and white blood cells, which are the body’s natural defense against infection. As the pocket of pus grows larger, it can put pressure on the surrounding tissues, leading to pain, swelling, and inflammation. When the pressure becomes too great, the abscess may rupture, causing a sudden release of pus and a sensation of relief from the pressure. However, while the rupture of an abscessed tooth may provide temporary relief, it is essential to seek prompt dental treatment to address the underlying infection and prevent the abscess from recurring.
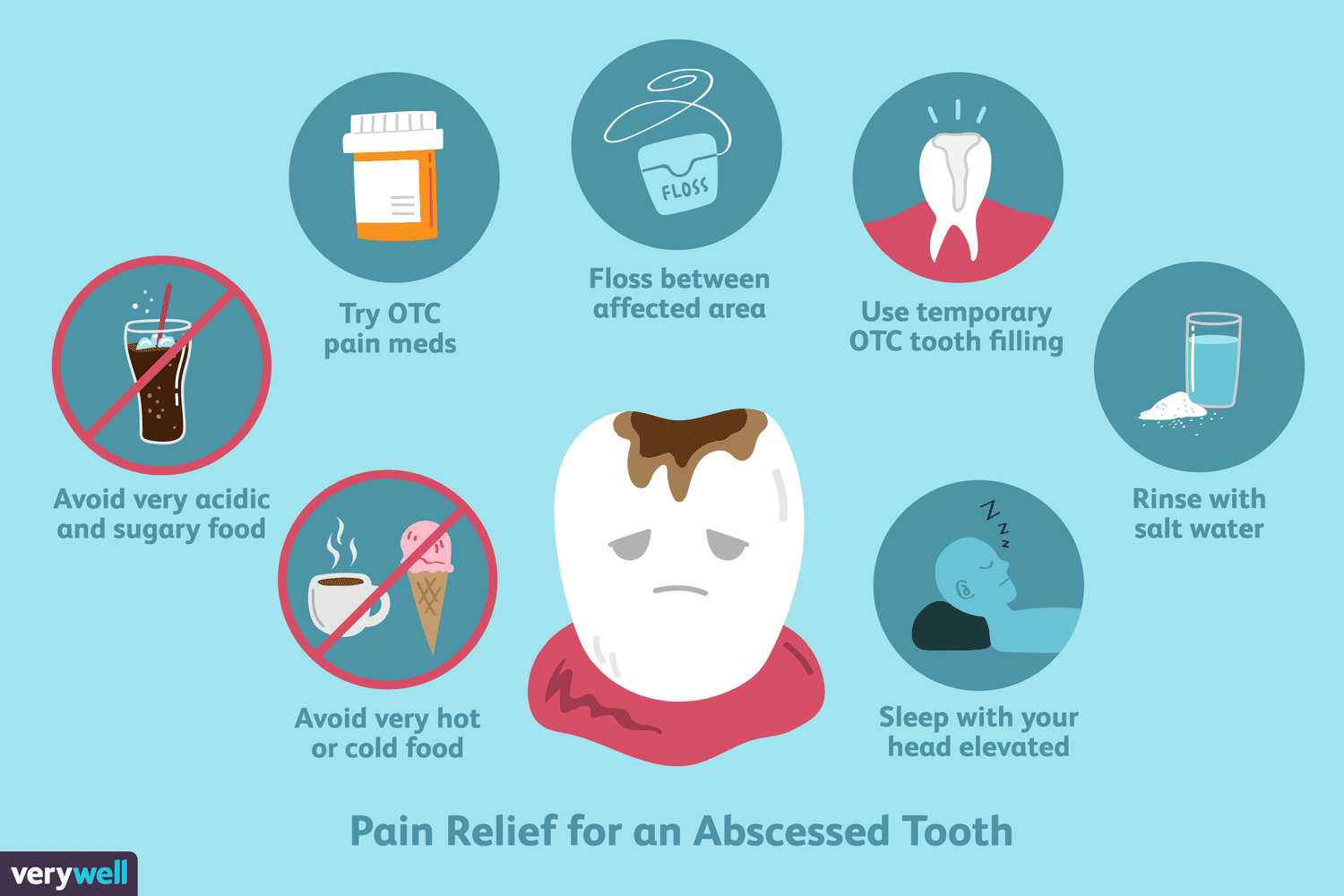
- Immediate steps to take if your abscessed tooth pops, including pain relief and infection control
If your abscessed tooth pops, it is essential to take immediate steps to control pain and infection. Here are some immediate steps you can take:
- Rinse your mouth with warm salt water: This can help to reduce pain and inflammation and flush out any debris from the abscess.
- Apply a cold compress: This can help to reduce swelling and discomfort. Use a clean cloth or a bag of ice wrapped in a towel and hold it against the affected area.
- Take pain relievers: Over-the-counter pain medications such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help to relieve pain and reduce fever.
- Avoid hot, cold, or hard foods: Stick to soft, lukewarm foods to prevent further irritation and pain.
- Keep the affected area clean: Brush your teeth gently and avoid touching the affected area with your tongue or fingers to prevent further infection.
- Seek dental care: Even if the abscess has ruptured and you are experiencing temporary relief, it is essential to seek prompt dental care to address the underlying infection and prevent the abscess from recurring. Your dentist may prescribe antibiotics or recommend drainage to treat the infection.
In summary, if your abscessed tooth pops, it is important to take immediate steps to control pain and infection and seek prompt dental care to address the underlying infection and prevent the abscess from returning.
- When to seek emergency dental care
While it is important to seek dental care as soon as possible if you have an abscessed tooth, there are certain situations where you may need to seek emergency dental care. If you experience any of the following symptoms, it is important to seek emergency dental care immediately:
- Severe pain: If you are experiencing severe, unbearable pain, it may be a sign that the infection has spread or that there is a complication that needs urgent attention.
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing: If the abscess is causing difficulty breathing or swallowing, seek immediate medical attention.
- Swelling in the face or neck: If you notice swelling in your face or neck, it could be a sign that the infection has spread, which requires immediate medical attention.
- High fever: If you have a high fever, it could be a sign that the infection has spread and is affecting other parts of your body, which requires urgent medical attention.
In short, if you experience any severe symptoms or complications related to an abscessed tooth, seek emergency dental care immediately to prevent the spread of infection and ensure prompt treatment.
Section 3: Treatment for an Abscessed Tooth
- How a dentist diagnoses an abscessed tooth
A dentist can diagnose an abscessed tooth through a variety of methods. The dentist will begin by performing a visual examination of the affected tooth and surrounding area to look for signs of infection, such as swelling or redness. They may also use a dental probe to check for sensitivity in the affected tooth or gums. Additionally, they may order X-rays or other imaging tests to get a more detailed look at the tooth and surrounding tissues. In some cases, the dentist may also perform a pulp vitality test to determine if the tooth’s pulp is infected. Once the dentist has diagnosed an abscessed tooth, they can recommend an appropriate treatment plan to address the infection and prevent it from spreading.
- Common treatments for an abscessed tooth, including antibiotics and drainage
There are several common treatments for an abscessed tooth, including:
- Antibiotics: If the abscessed tooth is caused by a bacterial infection, the dentist may prescribe antibiotics to help control the infection. Antibiotics can be taken orally or applied topically.
- Drainage: If the abscess has not ruptured, the dentist may need to drain the pus from the affected tooth. This can be done through a small incision in the gum tissue or by creating a small hole in the tooth.
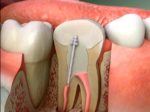
- Root canal therapy: In some cases, the dentist may recommend a root canal to remove the infected pulp and prevent the infection from spreading. This involves removing the infected tissue, cleaning and shaping the root canal, and filling it with a special material.
- Extraction: If the abscessed tooth is severely damaged or cannot be saved, the dentist may recommend extracting the tooth to prevent the infection from spreading to other teeth or parts of the body.
- Pain management: The dentist may also prescribe pain medications to help manage pain and discomfort associated with the abscessed tooth.
It is important to note that treatment for an abscessed tooth will depend on the severity of the infection and the underlying cause of the abscess. Therefore, it is essential to seek prompt dental care if you suspect you have an abscessed tooth to receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
- The importance of following through with treatment to prevent the abscess from returning
Following through with treatment is crucial to prevent the abscess from returning. If the underlying infection is not completely treated, the abscess can reform, causing more pain and damage to the affected tooth and surrounding tissues. In addition, an untreated abscess can lead to serious complications, such as the spread of infection to other parts of the body, tooth loss, and bone loss.
It is important to follow your dentist’s instructions for post-treatment care, such as taking prescribed medications and maintaining good oral hygiene. You may also need to attend follow-up appointments to monitor the healing process and ensure that the infection has been completely eradicated.
In addition to following through with treatment, it is important to practice good oral hygiene habits, such as brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and visiting the dentist regularly for checkups and cleanings. By maintaining good oral hygiene, you can prevent the development of tooth decay and gum disease, which can lead to abscesses.
In conclusion, following through with treatment is essential to prevent the abscess from returning and to protect your dental health. By working closely with your dentist and maintaining good oral hygiene habits, you can prevent the development of abscesses and other dental problems.
Section 4: Prevention of Abscessed Teeth
- Steps you can take to prevent an abscessed tooth from developing in the first place, including good oral hygiene habits and regular dental checkups
There are several steps you can take to prevent an abscessed tooth from developing in the first place, including:
- Practice good oral hygiene: Brush your teeth at least twice a day, floss daily, and use an antiseptic mouthwash to remove plaque and bacteria from your mouth.
- Visit your dentist regularly: Regular dental checkups and cleanings can help to identify and treat dental problems before they progress to more serious conditions.
- Address tooth decay and gum disease promptly: If you notice any signs of tooth decay or gum disease, such as tooth sensitivity or bleeding gums, seek dental care promptly to prevent the condition from worsening.
- Eat a healthy diet: Avoid sugary and acidic foods that can erode tooth enamel and contribute to tooth decay.
- Wear protective gear: If you participate in contact sports, wear a mouthguard to protect your teeth from trauma that can lead to abscesses.
By taking these steps, you can reduce your risk of developing an abscessed tooth and other dental problems. Remember, prevention is key to maintaining good oral health and preventing serious dental problems from developing.
- How to recognize the signs of an abscessed tooth and seek treatment promptly
Recognizing the signs of an abscessed tooth and seeking prompt dental care is essential to prevent the infection from worsening and causing serious complications. Here are some signs to look out for:
- Severe tooth pain that may radiate to the jawbone, ear or neck
- Swollen or red gums
- Tooth sensitivity to hot or cold foods and drinks
- Pain while chewing or biting
- Bad taste in the mouth
- Foul odor in the mouth
- Fever
- Swelling in the face or neck
- General feeling of being unwell
If you experience any of these signs or symptoms, it is important to seek dental care as soon as possible. Delaying treatment can cause the infection to spread and lead to serious complications, such as bone loss or tooth loss.
To seek treatment promptly, you can call your dentist and explain your symptoms to schedule an emergency appointment. Some dental practices offer emergency dental services outside of regular business hours, so be sure to ask if this is an option. If you cannot see your regular dentist, go to an emergency room or an urgent care clinic.
In summary, recognizing the signs of an abscessed tooth and seeking prompt dental care is essential to prevent the infection from worsening and causing serious complications. By being aware of the signs and symptoms of an abscessed tooth and seeking treatment promptly, you can protect your dental health and avoid more serious health problems.
Conclusion: An abscessed tooth is a serious dental condition that requires prompt treatment to prevent pain, swelling, and potential complications. If your abscessed tooth pops, it’s important to take immediate steps to control pain and infection and seek emergency dental care if necessary. By understanding the causes of an abscessed tooth and taking steps to prevent it from occurring, you can protect your dental health and enjoy a pain-free smile.